
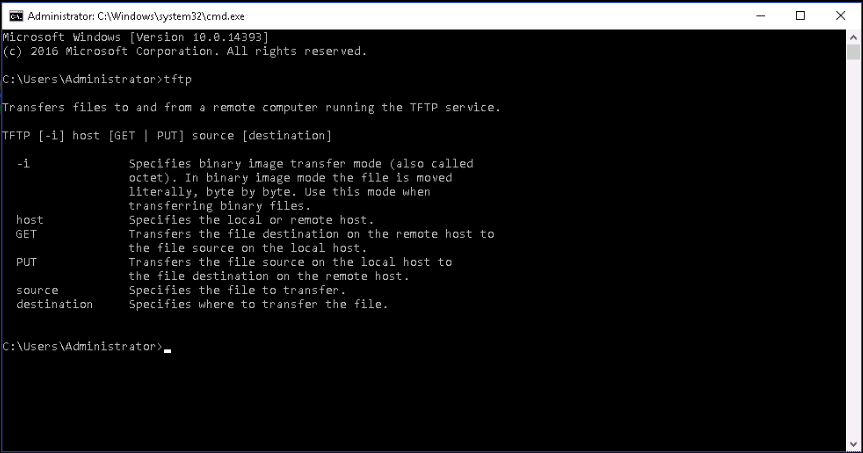
If the server is running on another port, say 8069, then the command syntax would be tftp -v 192.168.1.1 8069 -c put myfile theirfile You might also want to use the "-v" command parameter so that if something goes wrong you can see what it was: tftp -v 192.168.1.1 -c put myfile theirfile Where "myfile" is the name of the file you wish to upload and "theirfile" is the name that the file should have on the device.

Since the tftp default transfer mode is ASCII and you are uploading a ROM, the command should probably be tftp 192.168.1.1 -m binary -c put myfile theirfile Once you know the IP address of the device and the name of the file that it is expecting to receive, you should be able to upload the file to the device by using a command like tftp 192.168.1.1 -c put myfile theirfile
#TFTP CLIENT EXAMPLE INSTALL#
If you don't want to install the servers then some distribution have stand-alone TFPT clients, but they are usually not installed as part of the standard installation so you will have to install them manually. Most of the above mentioned TFTP server packages also install TFTP clients. So you need to have some documentation about the device to know how it configures itself. Another possibility is that the device configures an ad-hoc IP network. If the device configures itself using DHCP from a server on your network then you can look at the DHCP service log files to see what its IP address is. You might also need the port number on which the devices TFPT server is listening if it is not the TFTP well-known (standard) port, port 69.
If you are using Ubuntu, try this article by David Sudjiman. By using Network Component, you can very easily create or enhance applications with network features.
#TFTP CLIENT EXAMPLE CODE#
It is probably best to use the TFTP server (or "service" in MS parlance) that is "native" to the operating system distribution on which you wish to run the TFTP server. NET TFTP Client Sample Source Code Network Component provides an easy-to-use development interface to a variety of IP protocols.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
